Introduction
This article is all about ” Rosacea – Symptoms and causes.” In the vast spectrum of dermatological conditions, rosacea remains one of the most misunderstood and misdiagnosed ailments. This chronic skin condition predominantly affects the central face and is often mistaken for other skin issues such as acne, allergic reactions, or seborrheic dermatitis. Misconceptions about rosacea lead to inappropriate treatments, which can exacerbate the symptoms and cause further distress. A clear understanding of rosacea is essential for effective management and treatment.
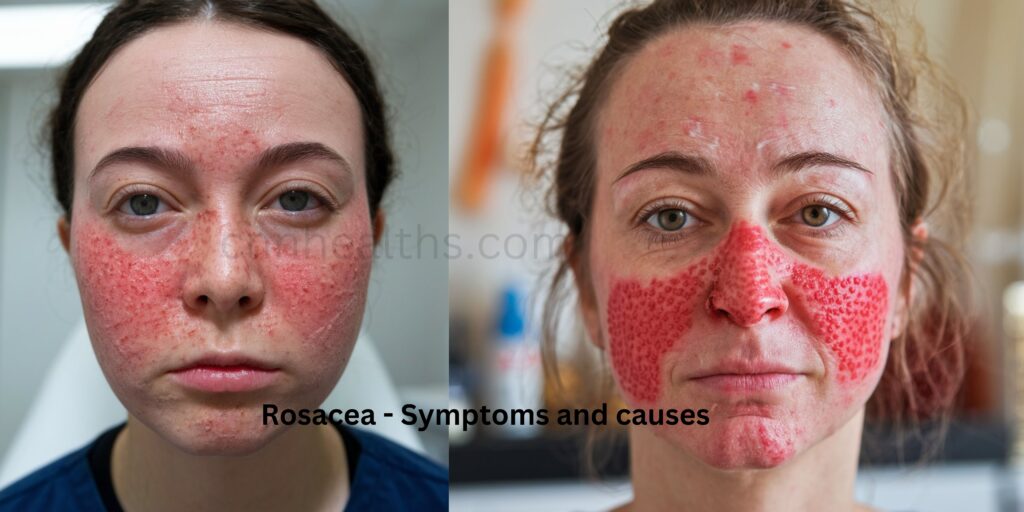
Rosacea is characterized by episodes of facial redness, visible blood vessels, and at times, small, red, pus-filled bumps. The condition tends to fluctuate, with periods of exacerbation and remission. Despite its prevalence, affecting millions globally, the exact cause of rosacea remains elusive. Researchers have identified several contributing factors, including genetic predisposition, immune system abnormalities, and environmental triggers.
Common Types of Rosacea:
1. Erythematotelangiectatic Rosacea:
– Persistent redness primarily on the cheeks and nose.
– Visible blood vessels.
2. Papulopustular Rosacea:
– Redness with swollen red bumps that resemble acne.
– Pus-filled blemishes.
3. Phymatous Rosacea:
– Thickened skin with a bumpy texture.
– Frequently affects the nose (rhinophyma).
4. Ocular Rosacea:
– Irritation and redness in the eyes.
– Eyelid swelling and recurrent eye infections.
Factors Contributing to Misdiagnosis
– Overlap with Other Conditions: Symptoms parallel those of acne and eczema, leading to incorrect identification.
Lack of Awareness: General public and some healthcare providers may have limited knowledge about the distinct characteristics of rosacea.
- Varied Presentation: Symptoms can vary greatly among individuals, making it challenging to recognize a single pattern.
Treatment should be tailored to the type and severity of rosacea. Approaches range from topical treatments to spoken medications, and in some cases, laser therapy. Lifestyle adjustments, recognizing and avoiding triggers, and gentle skincare routines also play crucial roles in managing rosacea effectively.
Understanding Rosacea: Myths vs. Facts
Rosacea, a chronic skin condition, is often misunderstood due to widespread myths. Clarifying these misconceptions with factual information is crucial for proper treatment.
Myths About Rosacea
Myth 1: Rosacea is Just grown person Acne
Many mistakenly believe rosacea is a form of grown person acne, but it’s a distinct condition. Unlike acne, rosacea primarily affects the face with redness, visible blood vessels, and sometimes swollen red bumps.
Myth 2: Rosacea Only Affects Fair-Skinned Individuals
While more common among fair-skinned individuals, rosacea can affect any skin type. Misunderstanding this can lead to underdiagnosis in people with darker skin tones.
Myth 3: Rosacea is Caused by Poor Hygiene
Poor hygiene does not cause rosacea. This misconception can be damaging, leading individuals to over-cleanse, which may aggravate the condition.
Myth 4: Rosacea is Contagious
Rosacea is not an infectious disease. It cannot be spread through contact, touching, or airborne particles.
Myth 5: Spicy Foods and soft drinks Cause Rosacea
Spicy foods and soft drinks can trigger rosacea flare-ups but are not root causes. Triggers vary among individuals, and sensitivity to these items doesn’t mean they cause the condition itself.
Facts About Rosacea
Fact 1: Genetic Predisposition Plays a Role
Genetics can contribute to rosacea development. If a family member has rosacea, there’s a higher chance of developing it, indicating genetic factors play a significant part.
Fact 2: Environmental Factors Can Worsen Symptoms
Sun exposure, extreme temperatures, and wind are environmental triggers that can exacerbate symptoms. Protection from these elements is a key management strategy.
Fact 3: No Cure, But Treatments Are Available
– sWhile there is no definitive cure for rosacea, various treatments exist, including topical and spoken medications, laser therapy, and lifestyle adjustments, which can manage and reduce symptoms effectively.
Fact 4: Rosacea Often Co-exists With Other Health Conditions
Research shows a correlation between rosacea and other medical conditions such as gastrointestinal diseases, cardiovascular diseases, and migraines.
Fact 5: Early Diagnosis Improves Management
Early diagnosis and intervention are vital. Recognizing early symptoms and seeking appropriate treatment can prevent the condition from worsening and improve quality of life.
Recognizing the Differences
Understanding the distinctions between myths and facts helps in managing rosacea more effectively. By demystifying these misconceptions, individuals can approach treatment with accurate knowledge and set realistic expectations for outcomes. Accurate education on rosacea is essential for both patients and healthcare providers to ensure optimal care.
The Different Types of Rosacea
Rosacea is not a monolithic condition; it presents itself in various forms, each with distinct characteristics and potential treatments. Understanding the different types can aid in proper diagnosis and management.
1. Erythematotelangiectatic Rosacea (ETR)
Symptoms: Persistent redness, visible blood vessels, and frequent flushing.
Characteristics Central facial redness, predominantly on the cheeks and nose.
Triggers Hot drinks, spicy foods, extreme temperatures, and emotional stress.
Treatment Topical therapies (brimonidine, metronidazole), spoken medications like doxycycline, and laser therapy to reduce visible blood vessels.
Papulopustular Rosacea
- Symptoms Redness with acne-like breakouts, primarily on the face.
Characteristics Swollen, red bumps resembling pimples, often misidentified as acne.
Triggers Similar to ETR, but may also include certain skin products.
Treatment Topical antibiotics (metronidazole, azelaic acid) and skincare regimens to reduce irritation.
3 . Phymatous Rosacea
Symptoms Skin thickening and a bumpy texture, particularly on the nose (rhinophyma).
Characteristics Enlarged pores, rough skin texture, and irregular tissue growth, most commonly affecting men.
- vTriggers : Not well-defined, but soft drinks and certain foods might exacerbate the condition.
- Treatment : Surgical options (laser, scalpel excision) to remove excess tissue, combined with medications to manage inflammation.
4. Ocular Rosacea
- Symptoms : Irritated, bloodshot eyes, swollen eyelids, and possible vision problems.
- Characteristics : Burning or stinging eyes, blurred vision, and conjunctivitis.
- Triggers : Wind, sun exposure, stress, and dietary factors.
- Treatment : Warm compresses, eyelid hygiene, lingual antibiotics, and artificial tears to alleviate dryness.
Understanding these subtypes and their unique presentations can significantly impact the effectiveness of treatment plans, minimizing the trial-and-error period many patients endure. Correct identification is essential for targeted treatments, as what works for one type might not be effective for another, emphasizing the need for personalized medical advice.
Common Triggers and Symptoms
Understanding the triggers and symptoms of rosacea is vital for accurate diagnosis and effective management. This section outlines frequent triggers and typical symptoms that individuals may experience.
Common Triggers
Rosacea triggers vary from person to person, but some common factors have been identified:
Environmental Factors:
– Sun exposure
– Wind
– Temperature extremes (hot or cold weather)
– Dietary Influences:
-Spicy foods
- Soft drinks beverages
– Hot drinks (e.g. coffee and tea)
– Emotional Triggers:
– Stress
– Anxiety
– Embarrassment
– Medical and Lifestyle Factors:
– Exercise
– Certain medications (e.g. steroids)
– Use of topical irritants (e.g. harsh skincare products)
Typical Symptoms
The symptoms of rosacea can be diverse and may fluctuate over time. Recognizing these symptoms is crucial for effective treatment and management:
1. Facial Redness:
– Persistent redness primarily affecting the central part of the face.
– May look similar to sunburn or blush.
2. Visible Blood Vessels:
– Broken blood vessels can become visible, especially on the nose and cheeks.
3. Swelling and Inflammation:
– Swollen, red bumps that may resemble acne.
– Can sometimes be filled with pus, but this is not typical acne.
4. Skin Thickening:
– In severe cases, skin on the nose may thicken (e.g. rhinophyma).
– This is more common in men than women.
5. Eye Problems:
– Dry, irritated, or swollen eyes.
– Inflammation of the eyelids (blepharitis) or conjunctivitis.
6. Burning or Stinging Sensations:
– Some individuals report burning, stinging, or itching on affected skin areas.
Subtypes
Rosacea is categorized into four primary subtypes, each with distinct symptoms:
– Erythematotelangiectatic Rosacea:
– Characterized by redness, flushing, and visible blood vessels.
– Papulopustular Rosacea:
– Manifests as redness with acne-like breakouts.
– Phymatous Rosacea:
– Marked by skin thickening and a bumpy texture, often affecting the nose.
– Ocular Rosacea:
– Affects the eyes, causing redness, irritation, and potentially more severe complications if untreated.
The Psychological Impact of Rosacea
Rosacea, often misunderstood as just a skin condition, has profound psychological consequences. Individuals with rosacea may experience feelings of self-consciousness, embarrassment, and social anxiety. They often navigate a myriad of emotional challenges attributable to the visible symptoms, including facial redness, bumps, and swelling.
Several studies have highlighted the prevalence of anxiety and depression among those suffering from rosacea. It impacts various aspects of their lives, from personal relationships to professional interactions. The frequent misunderstandings and misdiagnoses surrounding rosacea exacerbate these psychological burdens, as individuals often fail to receive appropriate treatment and support.
Symptoms like persistent facial redness and visible blood vessels can lead to:
– Low Self-Esteem: The constant concern about appearance diminishes self-confidence, affecting both personal and social engagements.
– Social Withdrawal:The visible nature of rosacea discourages individuals from participating in social events, leading to isolation.
– Workplace Challenges: Concerns about appearance may hinder performance and cause stress, impacting job satisfaction and career progression.
The stigma attached to visible skin conditions like rosacea can be debilitating. Many feel judged by their appearance, leading to a perpetuation of negative self-image and emotional distress.
Furthermore, the unpredictability of rosacea flare-ups adds to the psychological strain. Constantly worrying about when and where the next flare-up will occur can lead to chronic stress and anxiety.
Effective treatment should consider not only the physical but also the emotional and psychological well-being of the patient. Comfort health support, counseling, and coping strategies can significantly improve the quality of life for those affected by rosacea.
Enhancing public awareness and understanding of rosacea’s psychological impact is crucial. Healthcare providers should be trained to recognize and address these psychological aspects, offering comprehensive care that encompasses both dermatological and comfort health support. This holistic approach is vital for improving patient outcomes and alleviating the psychological burden associated with rosacea.
Diagnosis: How to Identify Rosacea Correctly
Correctly diagnosing rosacea involves careful clinical evaluation and may include ruling out other conditions. Medical professionals often use a combination of patient history, physical examination, and specific diagnostic criteria to make an accurate diagnosis. Here are key steps and considerations:
Clinical Evaluation
1. Patient History
– Document detailed descriptions of symptoms, triggers, and onset history.
– Investigate any known family history of rosacea or related skin conditions.
2. Physical Examination
– Inspect the skin on the face for common signs such as persistent redness, visible blood vessels, and inflammatory bumps.
– Check if rosacea symptoms are present around the eyes which may indicate ocular rosacea.
Diagnostic Criteria
Primary Features (one or more must be present)
– Flushing (Transient Erythema): Frequent flushing or blushing that tends to last longer than normal.
– Nontransient Erythema: Persistent redness that does not subside.
– Papules and Pustules: Acne-like breakouts.
– Telangiectasia:Visible, small blood vessels just under the skin.
Secondary Features (often, but not exclusively present)
– Burning or Stinging: Sensation of burning or stinging in affected areas.
– Edema: Swelling particularly in the facial area.
– Dry Appearance: Dry, rough patches.
– Ocular Manifestations: Eye symptoms including watery or bloodshot appearance.
– Plaques: Raised red patches without changes in the surrounding skin.
– Phymatous Changes: Skin thickening, particularly around the nose (rhinophyma).
Differential Diagnosis
Other skin disorders have symptoms similar to rosacea. To avoid misdiagnosis:
– Acne: Differentiate based on the presence of blackheads and whiteheads, usually absent in rosacea.
– Lupus Erythematosus:Often presents butterfly-shaped rash across the nose but requires serological indicators for confirmation.
– Seborrheic Dermatitis: Characterized by greasy scales and redness primarily on scalp and nasolabial folds.
– Photodamage: Chronic sun exposure results in telangiectasia, yet lacks inflammatory papules and pustules.
Diagnostic Tools
While rosacea diagnosis is typically clinical, certain assessments may assist in differentiation:
– Dermatoscopy:Enhanced visual inspection of skin lesions.
– Biopsy:Rarely required but may be utilized to distinguish from mimicking conditions.
– Blood Tests:To rule out lupus and other systemic conditions.
Thorough and accurate diagnosis is paramount in differentiating rosacea from other dermatological conditions, ensuring effective management and treatment options.
Effective Medical Treatments
A comprehensive approach to treating rosacea necessitates a combination of topical and systemic therapies. Consistent with dermatological guidelines, effective treatments can be divided into several categories:
1. Topical Medications:
– _Metronidazole_: Available in gel, cream, and lotion forms, metronidazole reduces inflammation and conspicious redness.
– _Azelaic Acid_: This anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial agent is effective in reducing swelling and bump formation.
– _Ivermectin_: Primarily targeting the Demodex mite, ivermectin possesses anti-inflammatory properties, helping to both reduce lesion count and alleviate skin discomfort.
2. Systemic Medications:
– _lingual Antibiotics_: Tetracyclines such as doxycycline and minocycline offer potent anti-inflammatory effects, essential for moderate to severe cases of rosacea.
– _Isotretinoin_ : For severe phymatous rosacea refractory to other treatments, low-dose isotretinoin may be beneficial, under stringent medical supervision.
3. Laser and Light Therapies:
– _Laser Therapy_: Devices like pulsed dye lasers and CO2 lasers can effectively target visible blood vessels and diminish persistent erythema.
– _Intense Pulsed Light (IPL) Therapy_: IPL serves to reduce diffuse redness and minimize the appearance of vascular irregularities.
4. Lifestyle Modifications:
– _Trigger Management_: Educating patients to identify and avoid triggers such as spicy foods, hot beverages, temperature extremes, and stressful situations.
– _Skincare Routine_: Utilizing gentle, non-irritating skin cleansers and sunscreen to protect sensitive skin from exacerbations.
5. Emerging Treatments:
– _Brimonidine_: A newer class, alpha-adrenergic agonists such as brimonidine gel, helps to selectively constrict blood vessels, temporarily reducing redness.
– _Oxymetazoline_: An alpha-adrenergic receptor agonist that provides sustained relief from facial erythema by causing vasoconstriction of superficial blood vessels.
Adopting a multidisciplinary strategy incorporating traditional treatments and emerging therapies can substantially improve the quality of life for patients with rosacea. Personalized treatment regimens tailored to individual patient presentations ensure optimal management and symptomatic relief.
Lifestyle Changes and Natural Remedies
In addressing rosacea, lifestyle changes and natural remedies play a critical role in managing symptoms. Although individual responses may vary, certain strategies have proven effective for many.
Diet and Nutrition
– Anti-Inflammatory Diet: Adopting an anti-inflammatory diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help reduce rosacea flare-ups.
– Avoid Triggers: Identifying and avoiding food triggers is essential.
– Hydration: Drinking adequate water supports skin hydration and overall health.
– Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as fish, flax seeds, and walnuts, may reduce inflammation and improve skin condition.
Skin Care Routine
– Gentle Cleanse: Use a mild, non-irritating cleanser to maintain skin balance without causing further irritation.
– Moisturization: A hypoallergenic moisturizer helps maintain the skin barrier and minimizes dryness.
– Sun Protection: Daily use of broad-spectrum sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher protects against ultraviolet radiation, a common trigger for rosacea.
– Avoid Irritants: Steer clear of products containing fragrances that can exacerbate symptoms.
Stress Management
– Relaxation Techniques: Practicing mindfulness, meditation, and yoga can help in reducing stress, a known trigger for rosacea flare-ups.
– Healthy Sleep Patterns: Ensuring sufficient, quality sleep supports overall health and reduces stress levels.
Natural Topicals
– Green Tea Extract: Rich in antioxidants, green tea extract can help reduce inflammation and redness.
– Aloe Vera: Known for its soothing properties, aloe vera can provide relief from irritation and moisturize the skin.
– Chamomile: Chamomile has anti-inflammatory and calming effects that may benefit rosacea-prone skin.
Physical Activity
– Moderate Exercise: While exercise is beneficial, it’s essential to avoid overheating, which can worsen rosacea. Opt for moderate, cool environments and stay hydrated.
– Post-Exercise Care: Washing the face with cool water post-exercise can prevent flare-ups caused by heat and sweat.
Environmental Adjustments
– Temperature Control: Avoid extreme temperatures. Use humidifiers in dry environments and fans or air conditioning in hot conditions.
– Protective Clothing: Wearing wide-brimmed hats and lightweight, breathable fabrics can shield the skin from harsh elements.
By incorporating these lifestyle changes and natural remedies, individuals can take significant steps in managing rosacea effectively.
Skincare Tips for Rosacea-Prone Skin
Gentle Cleansing:For those with rosacea-prone skin, a gentle, sulfate-free cleanser is essential. Harsh ingredients can exacerbate redness and irritation. It is advisable to cleanse twice daily, using lukewarm water and avoiding vigorous rubbing.
Moisturization:Hydration is crucial. Look for non-comedogenic, fragrance-free moisturizers that help restore the skin barrier without causing irritation. Ingredients such as hyaluronic acid and ceramides are beneficial.
Sun Protection: Daily application of a broad-spectrum sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher is non-negotiable. Mineral-based sunscreens with zinc oxide or titanium dioxide are preferable due to their reduced potential for irritation.
Avoid Triggers: Identifying and avoiding personal triggers is imperative. Maintaining a journal to track flare-ups can aid in recognizing these triggers.
Appropriate Use of Treatments: Consult a dermatologist for tailored treatments. Topical medications like metronidazole or azelaic acid may be recommended. lingual antibiotics or other prescription medications might be necessary for more severe cases.
Focus on Products with Soothing Ingredients: Products containing niacinamide, chamomile, green tea extract, and licorice extract can be soothing. Avoid products with artificial fragrances that can worsen symptoms.
Regular and Consistent Routine Consistency in skincare routines aids in managing rosacea. Sudden changes in products or introduction of new ingredients should be avoided. Patch testing new products is advisable.
Minimal Makeup: When using makeup, opt for non-comedogenic, fragrance-free, and hypoallergenic products. Mineral makeup is often recommended. Ensure thorough removal of makeup at the end of the day to prevent skin blockage.
Lifestyle Adjustments: Adequate hydration, balanced diet, and regular exercise can benefit skin health. Stress management techniques such as yoga or meditation may help minimize flare-ups.
Professional Treatments:Laser and light-based therapies provided by qualified dermatologists can reduce redness and visible blood vessels. Regular follow-ups with dermatologists ensure optimal management and adjustment of treatment protocols as needed.
Preventive Measures to Minimize Flare-Ups
Preventing flare-ups is a key strategy in managing rosacea effectively. Implementing a tailored regimen can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of symptoms. Here are several proactive measures to consider:
Skincare Routine
1. Gentle Cleansing:
– Use mild, fragrance-free cleansers.
– Avoid soaps with harsh chemicals or abrasive textures.
2. Moisturizing:
– Select non-comedogenic and hypoallergenic moisturizers.
– Reapply moisturizers regularly to maintain skin hydration.
3. Sun Protection:
– Apply broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher daily.
– Wear wide-brimmed hats and seek shade whenever possible.
Avoiding Triggers
1. Dietary Precautions:
– Identify and limit foods and beverages that trigger symptoms (e.g., spicy foods, soft drinks, hot drinks).
– Maintain a food diary to track potential triggers.
2. Environmental Control
– Stay in cool environments; avoid excessive heat and cold.
– Use humidifiers in dry seasons to maintain skin moisture.
3. Stress Management:
– Practice relaxation techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises.
– Maintain a well-balanced lifestyle to reduce stress levels.
Medical and Professional Interventions
1. Medication and Topicals:
– Follow prescribed treatments for rosacea, including lingual antibiotics, topical metronidazole, or azelaic acid.
– Consult a dermatologist for tailored medical advice.
2. Laser and Light Therapies:
– Consider undergoing professional laser or light therapy to reduce visible blood vessels and redness.
– Discuss potential benefits and risks with a qualified specialist.
3. Regular Check-ups:
– Schedule routine dermatological appointments to monitor skin condition.
– Adjust treatments as necessary under professional guidance.
Lifestyle Adjustments
1. Clothing Choices:
– Wear breathable, non-irritating fabrics like cotton.
– Avoid tight clothing that can irritate the skin.
2. Hygiene Practices:
– Avoid rubbing or massaging the face vigorously.
– Use soft towels and pat the skin dry gently after washing.
3. Personal Products:
– Opt for hypoallergenic and non-irritating makeup and skincare products.
– Perform patch tests before using new products.
Implementing these preventive measures can empower individuals with rosacea to manage their condition more effectively, ensuring better skin health and quality of life.
The Importance of Consulting a Dermatologist
Consulting a dermatologist is crucial when dealing with rosacea due to the complexity and individual variations of the condition. Dermatologists offer specialized expertise in diagnosing and treating skin disorders, and rosacea, being multifaceted, benefits from their professional insight.
Accurate Diagnosis
– Identification of Subtype: Dermatologists can identify the specific subtype of rosacea, whether it’s erythematotelangiectatic, papulopustular, phymatous, or ocular, which is essential for tailored treatment.
– Differential Diagnosis: They can differentiate rosacea from other skin conditions like acne, eczema, or lupus, ensuring appropriate treatment.
Personalized Treatment Plans
– Customized Medication: Dermatologists can prescribe the proper medication, such as topical treatments (metronidazole, azelaic acid) or lingual antibiotics that fit the patient’s specific needs.
– Advanced Therapies: They have access to advanced treatments like laser therapy, light therapy, and other emerging technologies that may not be available over-the-counter.
Monitoring and Adjustment
– Progress Tracking: Regular consultations allow dermatologists to monitor progress and make necessary adjustments to the treatment plan, maximizing effectiveness.
– Side Effect Management: Dermatologists can manage and mitigate potential side effects associated with treatments, ensuring patient safety.
Expertise in Skincare
– Product Recommendation: Dermatologists advise on suitable skincare products that won’t trigger rosacea, such as gentle cleansers and non-comedogenic moisturizers.
– Lifestyle Guidance: They provide valuable advice on lifestyle adjustments, including dietary changes and sun protection, which are critical in managing flare-ups.
Psychological Support
Living with rosacea can take a psychological toll. Dermatologists can refer patients to support groups or counselors, offering a holistic approach to managing the condition.
Long-term Management
Rosacea is a chronic condition requiring ongoing management. Dermatologists help patients develop long-term strategies, including recognizing triggers and coping mechanisms to maintain skin health over time.
Consulting a dermatologist ensures that rosacea is managed competently, reducing the risk of complications and enhancing the patient’s quality of life.
Success Stories: Real-Life Experiences
Rosacea, though often misunderstood, has seen many individuals successfully managing its symptoms through personalized treatments and lifestyle adjustments. These stories illustrate the journey from misdiagnosis to effective treatment.
Jane, a 34-year-old teacher, resist persistent facial redness and bumps for years. Initially misdiagnosed with acne, she felt frustrated by the lack of improvement. After consulting a dermatologist who accurately diagnosed her with rosacea, she began a regimen including topical metronidazole and lifestyle changes. Avoiding known triggers such as spicy foods and soft drinks Jane noticed a significant reduction in flare-ups within three months.
John, a 50-year-old IT professional, experienced frequent flushing and eye irritation. His rosacea was exacerbated by stress and long work hours in front of a computer screen. A comprehensive plan involving lingual antibiotics, laser therapy, and regular breaks from screen time helped him regain control. John’s improved complexion and reduced ocular symptoms enhanced his professional confidence and comfort.
Emily, a young professional in the marketing industry, struggled with rosacea’s impact on her social life. She discovered improvements through a combination of prescription treatments and incorporating gentle skincare products. Hydration, using sunscreen daily, and avoiding harsh exfoliants reduced her symptoms substantially. Emily’s story highlights the importance of individualized skincare routines.
David, a retiree, dealt with the psychological toll of rosacea. Misunderstood as excessive blushing, his condition affected his self-esteem and social interactions. Seeking support from online forums, David found solace and practical advice. His approach included dietary modifications, including reducing caffeine intake and incorporating anti-inflammatory foods. The community support coupled with a well-rounded treatment plan drastically improved his quality of life.
– These success stories emphasize the importance of accurate diagnosis, personalized treatment plans, and community support. They serve as a beacon of hope for anyone facing the challenges of rosacea.
Conclusion: Breaking the Stigma and Moving Forward
Breaking the stigma around rosacea involves a multi-faceted approach that encompasses education, open dialogue, and societal change. Misconceptions about rosacea contribute to the stigma, often leading to misunderstandings about its causes and treatments. Dispelling these myths is crucial for creating an inclusive and supportive environment for those affected by the condition.
A fundamental step in breaking the stigma is comprehensive education. Accurate information about rosacea, its triggers, symptoms, and treatment options should be widely disseminated. Educational campaigns can be conducted through various media, including social media platforms, healthcare websites, and community outreach programs.
Open dialogue is another crucial element. Encouraging individuals to share their experiences and challenges with rosacea can foster a sense of community and reduce feelings of isolation. Support groups, both online and offline, provide safe spaces for individuals to discuss their condition without fear of judgment.
Healthcare professionals play a pivotal role in breaking the stigma. They should be well-informed about the latest research and treatments for rosacea to provide accurate diagnoses and effective treatment plans. Empathy and understanding from healthcare providers can significantly impact a patient’s comfort level and willingness to seek treatment.
Society as a whole must shift its perception of rosacea. Media representation of individuals with rosacea should focus on normalizing the condition rather than portraying it negatively. Public figures and influencers who openly discuss their experiences with rosacea can also help in reducing stigma and promoting acceptance.
There are several actionable steps that can be taken:
– Educational Campaigns: Disseminate accurate information through various channels.
– Support Groups: Establish and promote support groups for individuals with rosacea.
– Healthcare Training: Educate healthcare professionals about the condition.
– Positive Representation: Encourage media and influencers to portray rosacea positively.
Breaking the stigma surrounding rosacea is a collective effort that requires involvement from individuals, healthcare professionals, and society. By fostering an environment of understanding and support, it is possible to improve the quality of life for those affected by rosacea and encourage them to seek effective treatment without fear or shame.